In the realm of Zoroastrianism, the sacred rituals hold a paramount position, intricately intertwined with the celestial rhythms of the Zoroastrian calendar.
This article delves into the profound significance of these rituals and their harmonious alignment with the cosmic tapestry.
From birth rituals that symbolize new beginnings to ceremonies honoring ancestors and the deceased, these meticulous practices ensure spiritual purification and maintain an enduring sense of harmony.
Join us on a scholarly exploration of the sacred rituals and their profound connection to the Zoroastrian calendar.
Key Takeaways
- Rituals in Zoroastrianism foster community and spiritual connection.
- The Zoroastrian calendar determines the timing of religious observances and reflects the close connection between nature and spiritual beliefs.
- Celestial events serve as powerful omens and reaffirm the harmonious relationship between celestial and terrestrial realms.
- Seasonal celebrations in Zoroastrianism are closely aligned with nature and mark significant transitions.
The Importance of Rituals in Zoroastrianism


The importance of rituals in Zoroastrianism is evident through their role in fostering a strong sense of community and spiritual connection. Rituals hold a significant place in the religious practice of Zoroastrians, serving as a means to express devotion, reinforce cultural identity, and establish a connection with the divine. The symbolism of rituals is deeply ingrained in the faith, with each action and gesture carrying a specific meaning.
These rituals hold cultural significance as they provide a framework for Zoroastrians to celebrate important milestones and events in their lives. From birth and initiation ceremonies to marriage and death rituals, these practices serve to reinforce the cultural identity of the community and provide a sense of belonging. The rituals also act as a means of passing down traditions and teachings from one generation to the next.
Moreover, rituals in Zoroastrianism hold a spiritual significance. They serve as a way to connect with Ahura Mazda, the supreme deity, and seek blessings and guidance. Through the performance of rituals, Zoroastrians believe they can purify their souls, ward off evil, and strengthen their connection with the divine.
Overall, rituals in Zoroastrianism play a vital role in maintaining cultural traditions, fostering a sense of community, and establishing a spiritual connection with the divine. They serve as a means through which Zoroastrians express their devotion, reinforce their cultural identity, and seek spiritual blessings and guidance.
Understanding the Zoroastrian Calendar


The Zoroastrian calendar is a solar calendar that plays an essential role in the religious practices of followers of Zoroastrianism. It is based on the movements of the sun and the alignment of celestial events, such as equinoxes and solstices.
The calendar not only helps determine the timing of religious observances but also reflects the close connection between nature, seasons, and the spiritual beliefs of Zoroastrians.
Significance of Celestial Events
Eclipses, meteor showers, and planetary alignments frequently captivate the attention of Zoroastrian scholars, who fervently study these celestial phenomena to discern their significance within the complex mechanics of the Zoroastrian calendar. These cosmic phenomena are not merely observed for their aesthetic appeal but hold deep spiritual and symbolic meanings for the Zoroastrian community.
-
Harbingers of Change: Celestial events often serve as powerful omens in the Zoroastrian tradition, signaling the onset of significant changes or transitions in the world. They are believed to convey messages from the divine and guide the faithful in their spiritual journey.
-
Alignment with Divine Order: The occurrence of celestial events in alignment with specific festivals or ceremonies within the Zoroastrian calendar is seen as a reaffirmation of the divine order and the harmonious relationship between the celestial and terrestrial realms.
-
Cosmic Balance and Renewal: These events also reflect the cyclical nature of the universe and symbolize the constant process of renewal and balance in Zoroastrian cosmology.
Seasons and Religious Observances
An important aspect of understanding the Zoroastrian calendar is recognizing how the changing seasons and religious observances are intricately intertwined. The Zoroastrian calendar, known as the Shahenshahi calendar, is based on the solar year and consists of twelve months, each with thirty days. The calendar also includes five intercalary days, known as Gatha days, which are dedicated to the recitation of sacred hymns.
Seasonal celebrations play a significant role in Zoroastrianism, with traditional customs and rituals that are closely aligned with nature and the changing seasons. For example, the festival of Norouz marks the arrival of spring and the New Year. During this time, Zoroastrians engage in various rituals such as house cleaning, setting up a Haft Seen table, and jumping over bonfires to ward off evil spirits.
Similarly, the festival of Mehregan celebrates the autumn harvest and is a time for giving thanks and expressing gratitude.
Birth Rituals and Their Significance


Birth rituals hold great significance in many cultures, as they are steeped in symbolism and serve as a way to honor the arrival of a new life.
These rituals not only mark the transition from pregnancy to parenthood, but also carry cultural importance in terms of passing down traditions and values to the next generation.
Furthermore, birth rituals often involve the participation of the community, highlighting the role of collective support and celebration in welcoming a new member into society.
Symbolism of Birth Rituals
Significantly, birth rituals in various cultures often serve as symbolic ceremonies that mark the beginning of a new life and the transition into parenthood. These rituals are deeply rooted in cultural traditions and beliefs, reflecting the unique perspectives and values of different societies.
The symbolism of rebirth is a common thread that runs through many birth rituals, representing the cycle of life and the renewal of the human spirit. Cultural diversity in birth rituals is evident in the various customs and practices observed around the world. Some examples include the Hindu tradition of performing the sacred thread ceremony, the Jewish tradition of the brit milah, and the Navajo tradition of the Baby Blessingway.
These rituals not only celebrate the arrival of a new life but also reinforce cultural identity and the importance of community support during this significant milestone in a family’s life.
Cultural Importance of Birth Rituals
The cultural importance of birth rituals lies in their ability to foster a sense of belonging and reinforce community bonds.
Birth rituals are deeply ingrained in cultural diversity and are practiced worldwide as traditional practices. These rituals vary across different cultures, reflecting the unique customs and beliefs of each society.
For example, in some cultures, there are specific rituals performed during pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period. These rituals often involve the participation of family members, community elders, and religious leaders. They serve to celebrate the arrival of a new life, provide support to the mother and the newborn, and transmit cultural values and traditions to the next generation.
Through birth rituals, communities come together to honor and welcome new members, thereby strengthening their collective identity and reinforcing the bonds that hold them together.
Role of Community in Birth Rituals
Communities actively participate in and contribute to birth rituals, creating a sense of unity and reinforcing cultural traditions. These rituals hold significant importance within various cultures and are often deeply rooted in traditional practices. The role of community support during birth rituals cannot be overstated, as it provides emotional and practical assistance to the parents and strengthens the bond between community members.
To convey a deeper understanding of the topic, consider the following points:
-
Emotional support: Communities provide a support system for expecting parents, offering encouragement and reassurance throughout the journey.
-
Knowledge sharing: Traditional practices are passed down through generations within communities, ensuring the preservation of cultural heritage and wisdom.
-
Sense of belonging: Birth rituals foster a sense of unity and belonging within the community, strengthening social bonds and creating a shared identity.
Rituals for Spiritual Cleansing and Purification


Interestingly, various cultures have developed unique rituals for spiritual cleansing and purification, which are believed to purify the soul and enhance spiritual well-being. These rituals have been passed down through generations and are often rooted in traditional practices. Spiritual purification is an important aspect of many religious and spiritual traditions, as it is believed to cleanse the individual of negative energies, sins, or impurities, allowing for a deeper connection to the divine.
In traditional practices, spiritual purification rituals can take many forms. In some cultures, bathing in sacred waters or rivers is believed to cleanse the body and soul. Others may use herbs, incense, or sacred objects to purify their surroundings and themselves. Prayer, meditation, and chanting are also common methods of spiritual purification, as they help to calm the mind and focus one’s intentions on spiritual growth and enlightenment.
These rituals often have specific guidelines or procedures that must be followed, ensuring that the purification process is carried out correctly. They may be performed individually or as part of a community ceremony, bringing people together in a shared experience of spiritual cleansing and renewal.
Overall, spiritual purification rituals are an integral part of many cultures and religions. They provide a means for individuals to cleanse their souls, release negative energies, and connect with their spiritual selves. These practices offer a sense of renewal, peace, and spiritual well-being, helping individuals to navigate the challenges of life with a greater sense of purpose and clarity.
Festivals and Celebrations in the Zoroastrian Calendar


Zoroastrian festivals and celebrations, rooted in ancient traditions, are marked by vibrant rituals and joyful gatherings that bring the community together. These festivals are an integral part of Zoroastrianism, with each celebration holding a significant meaning and purpose.
The historical origins of Zoroastrian celebrations can be traced back to the ancient Persian civilization, where Zoroastrianism originated. The festivals are closely tied to the Zoroastrian calendar, which is based on the solar year and consists of twelve months.
Here are three sub-lists that convey a deeper meaning of the festivals and traditions in Zoroastrianism:
-
Major Festivals:
- Nowruz: The Persian New Year, celebrated on the spring equinox, symbolizes renewal and the victory of light over darkness.
- Mehregan: This festival honors Mithra, the angel of friendship, and celebrates the bounty of harvest.
- Sadeh: A mid-winter festival that commemorates the discovery of fire and represents the triumph of warmth and light over cold and darkness.
-
Rituals and Ceremonies:
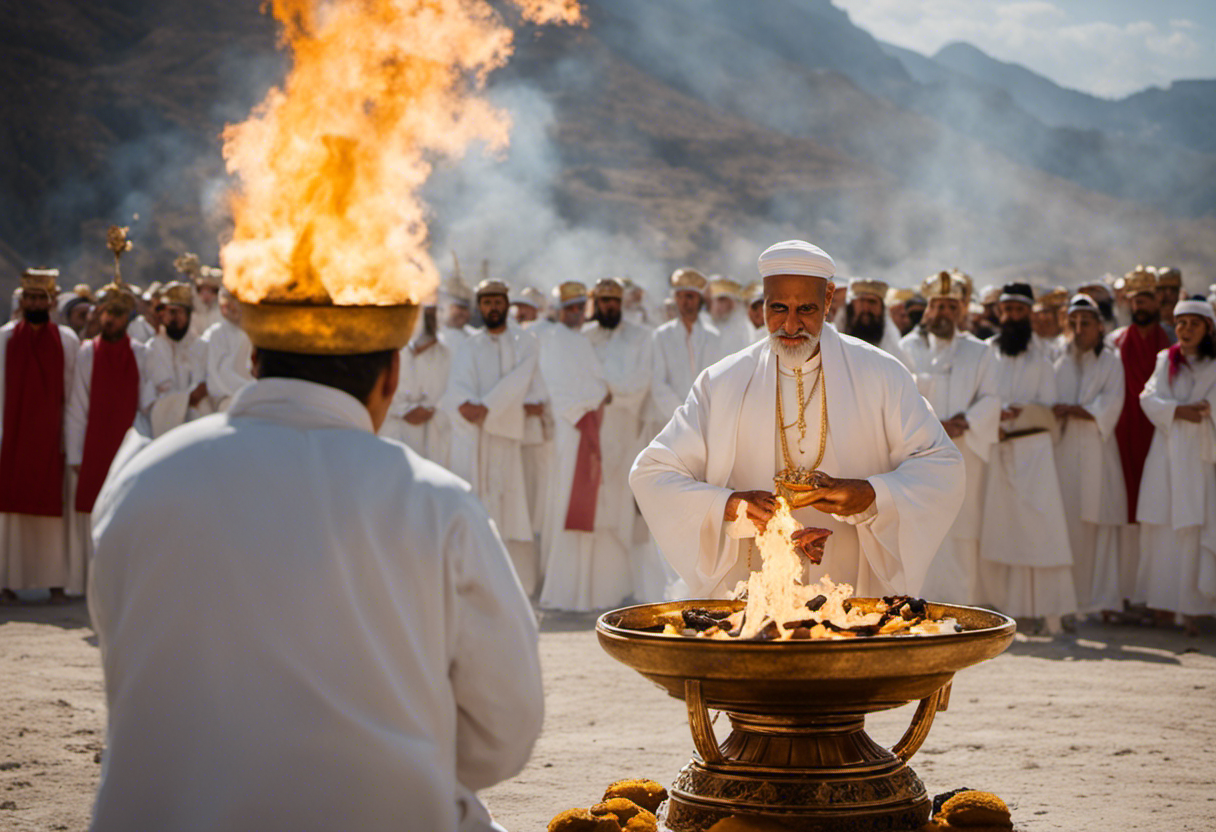
- Jashan: A ritual ceremony conducted in temples to honor the divine beings and seek their blessings.
- Yasna: A purification ritual performed by priests to maintain the spiritual purity of the community.
- Gahanbar: Seasonal festivals celebrated to express gratitude for the blessings of nature.
-
Community Gatherings:
- Navjote: The initiation ceremony where young Zoroastrians enter the faith, accompanied by family and friends.
- Wedding Celebrations: A joyous occasion where two individuals join in matrimony, celebrated with traditional customs and rituals.
- Funeral Rituals: A somber gathering where the community comes together to mourn the loss of a loved one and provide support to the bereaved family.
These festivals and celebrations play a vital role in preserving Zoroastrian traditions and fostering a sense of unity among the community. They serve as a reminder of the rich heritage and spiritual values that are deeply ingrained in Zoroastrianism.
Rituals for Honoring the Ancestors and the Deceased


During funeral rituals, the Zoroastrian community comes together to pay homage to their ancestors and provide solace to the grieving families. Ancestral remembrance is an important aspect of Zoroastrianism, as it allows individuals to connect with their past and honor the legacy of their forefathers. Funeral customs in this community vary depending on cultural and regional differences, but they all share a common goal of ensuring a peaceful transition for the deceased and offering support to the bereaved.
One of the key funeral customs in the Zoroastrian tradition is the exposure of the deceased to the elements, known as ‘sky burial’ or ‘Tower of Silence.’ This practice is rooted in the belief that the body, once lifeless, becomes impure and should not contaminate the earth or water. Instead, it is placed atop a tower or hill, where it is exposed to vultures and other scavenging birds, who consume the flesh and aid in the purification process.
Another significant aspect of Zoroastrian funeral rituals is the recitation of prayers, known as the Vendidad, which is a collection of texts that guide individuals on how to lead a righteous life. These prayers are recited by priests and family members during the funeral ceremony, with the intention of providing spiritual guidance and comfort to the deceased.
Overall, funeral customs in the Zoroastrian community serve as a means of honoring the deceased and providing solace to the grieving families. The rituals, such as sky burials and the recitation of prayers, are deeply rooted in the Zoroastrian belief system and aim to ensure a peaceful transition for the departed souls.
The Role of Rituals in Maintaining Spiritual Harmony


Rituals play a vital role in fostering spiritual harmony, as they not only provide a sense of structure but also facilitate a deeper connection with the divine. They have been practiced by various cultures and religions throughout history, serving as a means to connect with the spiritual realm and to cultivate personal growth.
The role of rituals in personal growth is multifaceted and encompasses several key aspects:
-
Creating a Sacred Space: Rituals often involve creating a designated space where individuals can focus their attention and intention. This sacred space provides a conducive environment for deep introspection and spiritual connection.
-
Establishing Routines: Rituals provide a sense of structure and routine in our lives. By incorporating regular practices into our daily or weekly routines, we can develop a sense of discipline and commitment to our spiritual growth.
-
Facilitating Transformation: The transformative power of ritual experiences lies in their ability to create a shift in consciousness. Through rituals, individuals can tap into their inner wisdom, release negative energies, and cultivate positive qualities such as gratitude, compassion, and resilience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the sacred rituals of Zoroastrianism hold great importance and are intricately aligned with the Zoroastrian calendar.
These rituals serve various purposes, from honoring ancestors and the deceased to spiritual cleansing and purification.
They play a vital role in maintaining spiritual harmony within the community.
The rich symbolism embedded within these rituals provides a profound and meaningful connection to the faith for its followers, creating a tapestry of beliefs and practices that are deeply rooted in the Zoroastrian tradition.